[email protected] 0750 441 2721
- Home
- About
- Academics
- Admissions
- Directories
- Research
- Alumni
- Activities
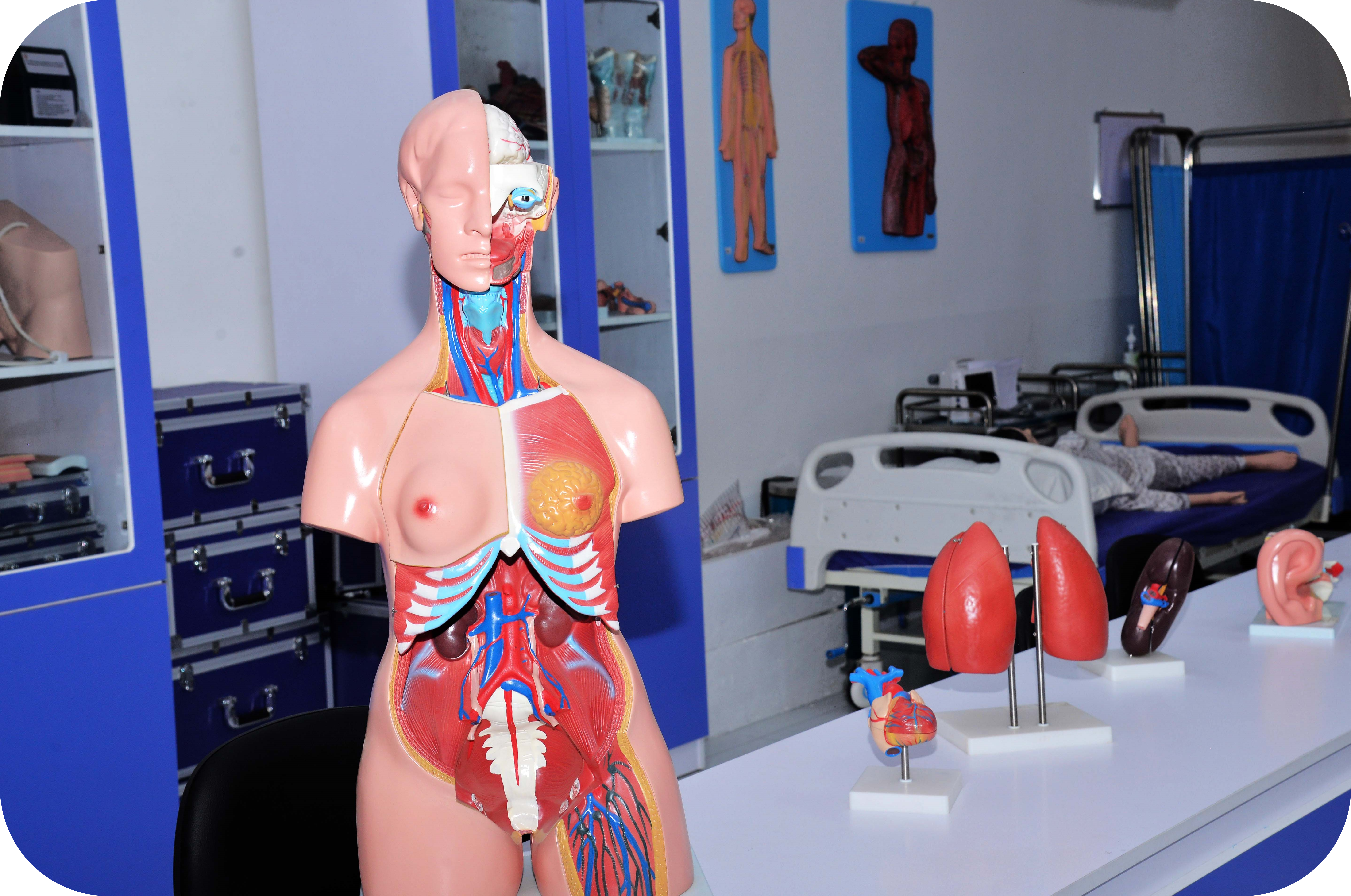
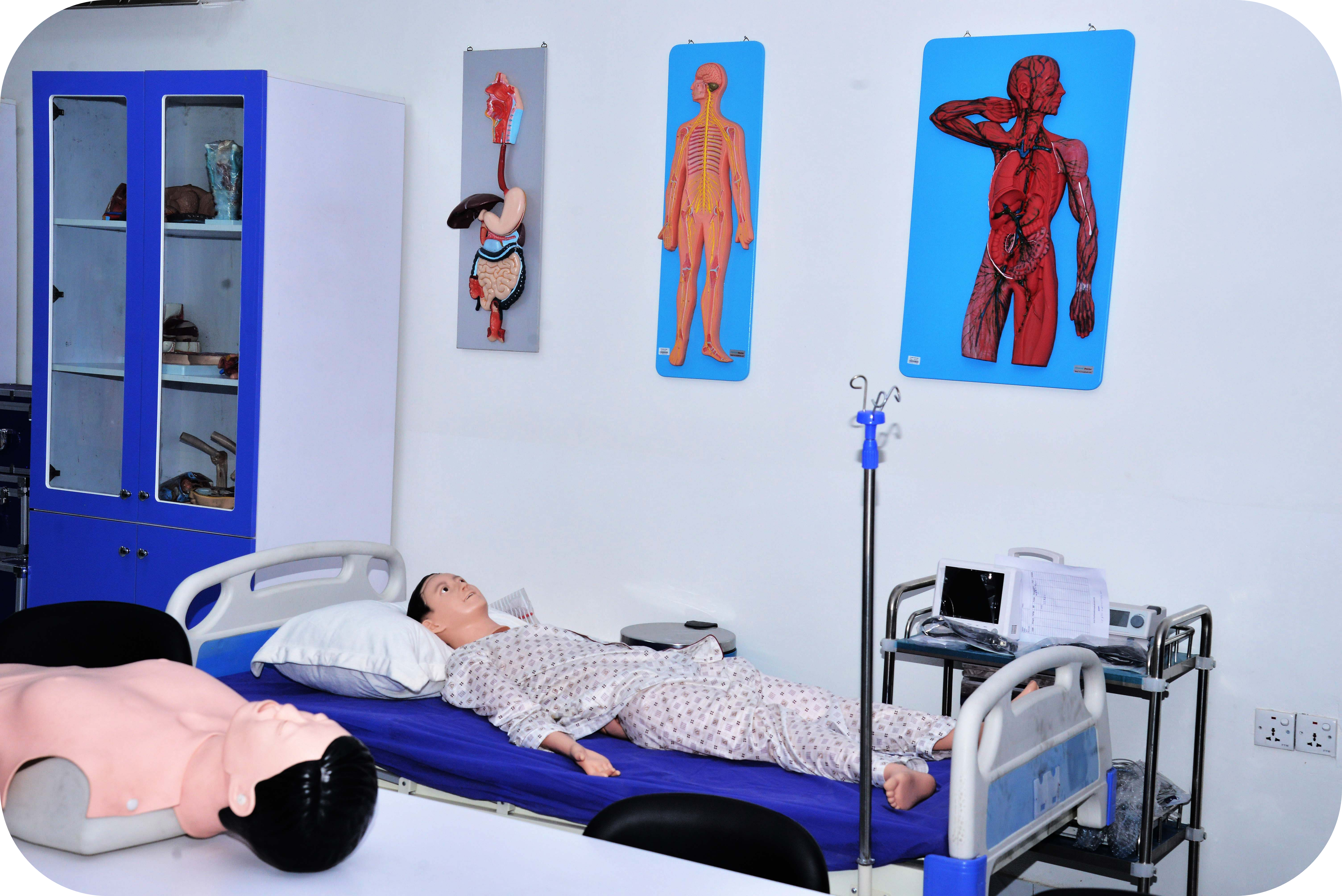
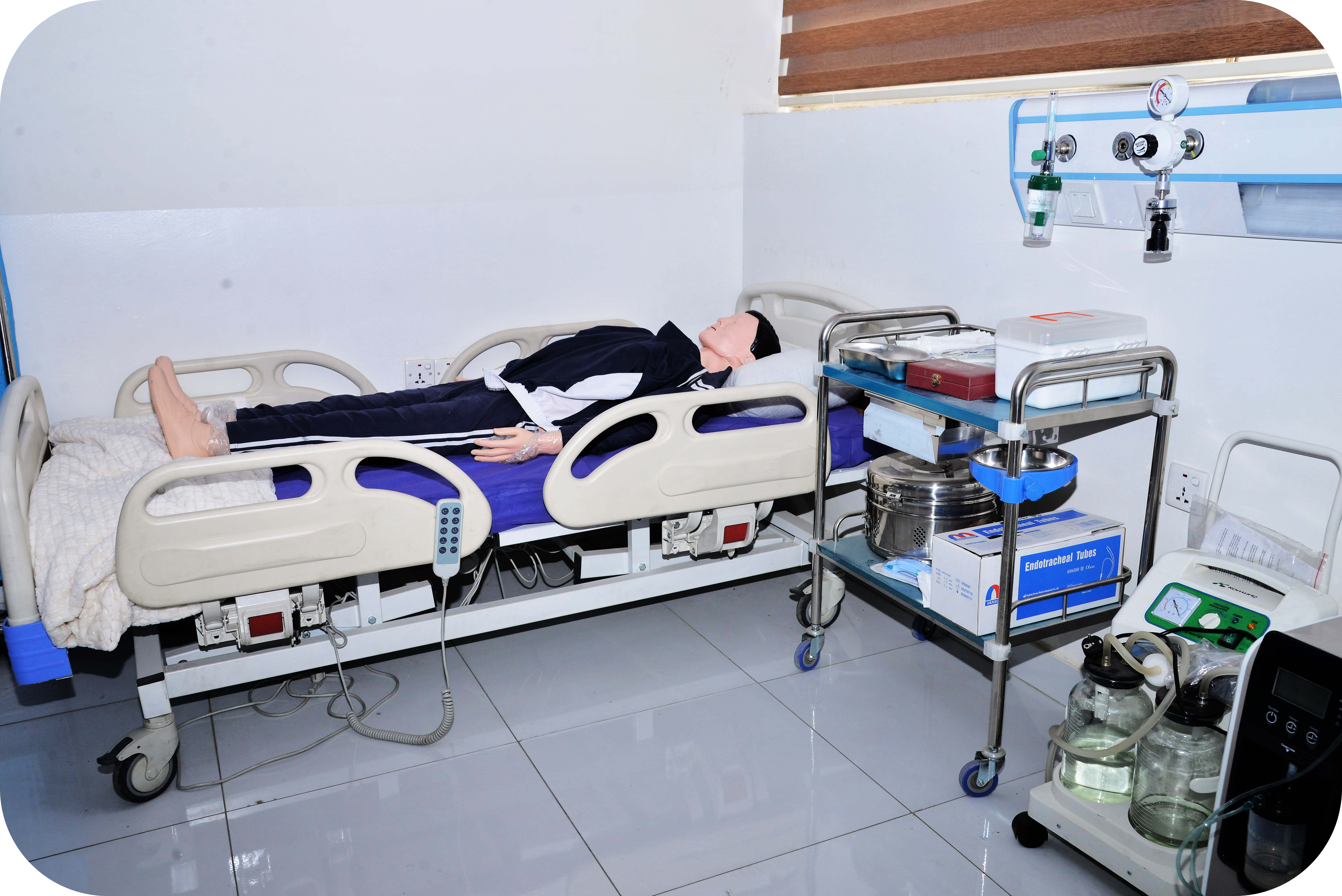
A medical laboratory, also known as a clinical laboratory, is a facility that performs tests on clinical specimens to collect information about a patient’s health in order to aid in illness diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. Clinical medical laboratories, as opposed to research laboratories that focus on basic science, such as those found in some academic institutions, are examples of applied science.
Medical laboratories come in all shapes and sizes, and they provide a wide range of diagnostic services. Acute-care hospitals and medical centers offer more comprehensive services, with laboratory testing accounting for 70% of clinical decisions. More basic testing services may be available in doctor’s offices and clinics, as well as skilled nursing and long-term care institutions. Medical laboratories that are for profit are known as commercial laboratories.